Various types of organic fertilizers are used in agriculture. Organic fertilizers are made from animal material and natural plants. Organic fertilizers usage in agriculture is more environment-friendly than chemical fertilizers.
Manure, compost, bone meal, vermicompost, and rock phosphate, are organic fertilizers used in organic farming. Organic fertilizers are generally made up of single ingredients and can be adapted to the specific nutritional needs of your plants.
Organic fertilizers are complex in biological structure, which is their main advantage. The fertilizers need the time and help of soil organisms to break down into simpler molecules.
The breakdown is a slow process and ensures complete and timely consumption of nutrients, unlike chemical fertilizers.
Organic fertilizers are more economical than chemical fertilizers. Farmers can prepare them locally at their farms. Also, organic fertilizers are made of renewable materials that are always available.
Different Types of Organic Fertilizers
These organic fertilizers, available to farmers, provide essential nutrients to plants for good crop yield.
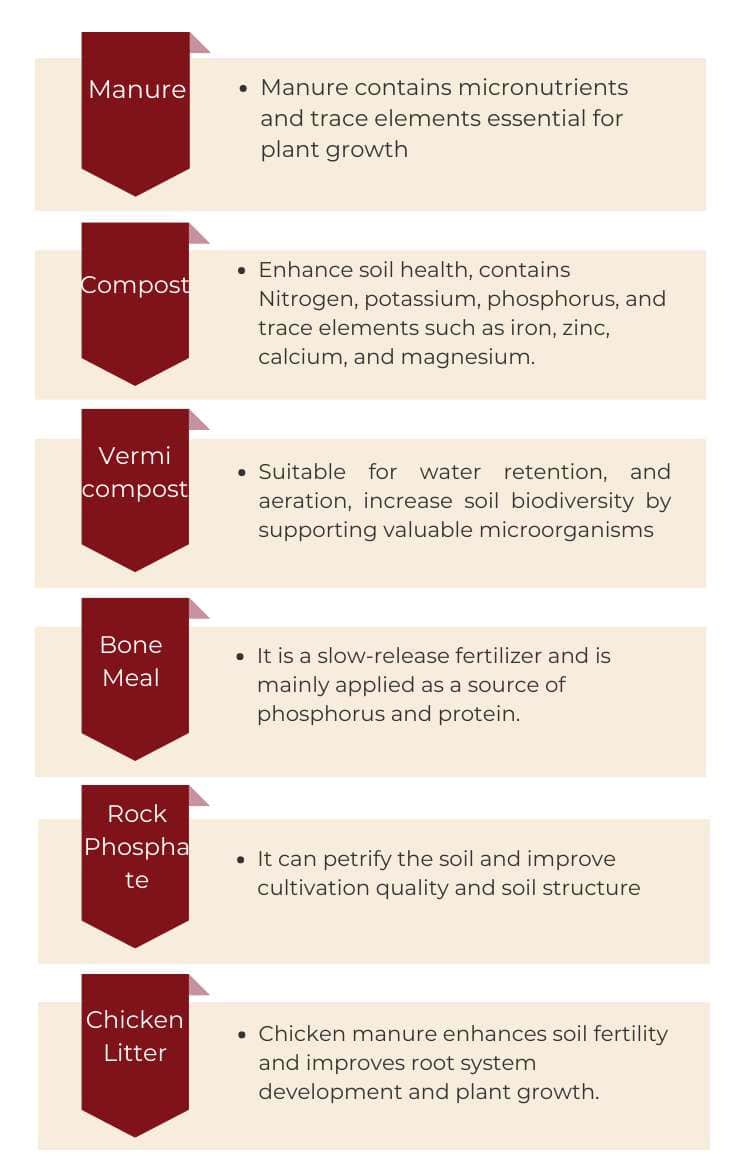
Manure
Manure is an organic material used as organic fertilizer in agriculture. It mainly consists of animal waste. Green manure and compost are other sources.
Manure increases soil fertility by providing organic matter and nutrients like nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus. Bacteria, fungi, and other organisms in the soil use nitrogen.
Manure is nutrient-rich organic fertilizer, including micronutrients and trace elements essential for plant growth. Manure contains approximately 70- to 80 percent nitrogen, 60 to 85 percent phosphorus, and 80 to 90 percent potassium. [1]
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are necessary for healthy crops and good yield. Plants do not recognize the source of the nutrients. However, compared to chemical fertilizers, organic fertilizers contain organic carbon, which plays a vital role in maintaining soil health, water retention, and soil tilth.
Micronutrients are present in manure, needed by crops. Manure has the potential to grow high-quality produce. It helps reduce soil erosion by enhancing soil quality. Manure is like an asset for a farmer, saving crop growing costs and making agriculture profitable.
Since manure is made of organic matter, it does not cause any pollution. Practically it reduces the amount of waste in agriculture by converting waste materials into organic fertilizer.
Compost
Compost is an organic matter mixture that provides nutrients to plants and enhances soil quality. Compost is made by decomposing food waste plants and recycling organic matter. Compost is a nutrient-rich mixture beneficial to organisms like worms.
Composite making requires a collection of green and brown natural materials. Green materials are those substances that have high nitrogen content, such as grass, food scraps, and leaves. Brown materials are woody and are excellent in carbon, such as wood chips, paper, and stalks.
Water is sprayed on green and brown materials to decompose into humus by microorganisms.
Composite enhance soil health. Nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, and trace elements such as iron, zinc, calcium, and magnesium are present in the composite.
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are the primary nutrients required for crop production. Research shows that compost enhances the soil’s water retention capacity and productivity. [2]
Composite conserve water resources, reduce waste, and cut methane emission. It also saves chemical fertilizer expenses.
Also Read: Types of Organic Farming Practices
Vermicompost
Vermicompost is one of the type of organic fertilizers. Various beneficial plant nutrients are present in vermicomposts, such as Nitrogen, Potassium, Phosphorus, and other helpful soil microbes.
Earthworms such as red, white, and other worms decompose food waste and bedding to form vermicompost.
Decomposing waste material using worms is called vermiculture, and the rearing of worms for this purpose is called vermiculture.
Vermicompost is suitable for water retention, aeration, and microbial activity. It is rich in nutrients such as and has buffering capacity.
Vermicompost increases soil biodiversity by supporting valuable microorganisms, which promote plant growth by directly producing hormones and enzymes that control plant growth. [3]
Indirectly vermicompost controls plant pathogens and nematodes, thus improving plant health and lowering yield loss. Because of vermicompost’s natural biological, biochemical, and physicochemical properties, it can support sustainable agriculture and is safe for the environment.
Bone Meal
Bone meal organic fertilizer is made by drying animal bones and grinding them into a powder or granules used on plants or crops. Bone meal is rich in phosphorus and calcium, so it is used as an organic fertilizer for plants.
It is a slow-release fertilizer and is mainly applied as a source of phosphorus and protein.
Bones are excellent in nutrients and minerals; using bone meal for plants will help them grow healthy and more vigorously. However, bone meal is not appropriate in every condition.
The proportion of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium (NPK) in bone meal can vary considerably depending on the source. It ranges from 3-15-0 to 2-22-0, although some steamed bone meals contain a 1-13-0 NPK ratio.
Bone meal also contains a good amount of calcium but does not provide enough nitrogen for plants. According to Colorado State University research, plants get phosphorus only from the bone meal if the soil acidity is below 7.0. [4]
Rock Phosphate
Grounding rocks make rock phosphate, rich in phosphate and other beneficial nutrients for plants. It is among the types of organic fertilizers.
Like green sand, rock phosphate can petrify the soil and improve cultivation quality and soil structure. [5]
However, its primary use is to increase phosphate fertility in the soil where phosphate concentration is low and increase root activity in transplants and germinating seeds.
Rock phosphate organic fertilizer is nutrient-rich and works with the soil, and the nutrients are then available to the plants evenly throughout the growing season.
Rock phosphate fertilizer’s main advantage is the insoluble elements in the water. Instead, the components sit on the ground until plants use them to grow there.
Chicken Litter
Chicken litter is a waste from poultry farming, mainly containing poultry manure, but it also has livestock feed, straw, and feathers, which are used as bedding in poultry rearing. Sawdust, ground sugar cane, wood chips, and peanut hulls are commonly used to form beds in poultry farming.
Chicken litter is one of the best organic fertilizer types and a valuable nutrient source. Chicken waste contains approximately 4 percent water, 3 percent nitrogen, 2.5 percent phosphate, and 1.8% potash.
Chicken manure enhances soil fertility and improves root system development and plant growth, making them less prone to disease and pest attacks. Poultry manure rapidly mineralizes in the soil and creates high temperatures; therefore, use in the summer is not recommended.
Conclusion
In recent years, increasing attention has been paid to replacing chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers to maintain high yields and protect the environment.
Several types of organic fertilizers provide different essential nutrients to plants for good growth and yield. You can make organic fertilizer at home using food waste, which is also available commercially.
Study shows that using organic fertilizers minimizes chemical fertilizers and contributes to agricultural ecosystems’ long-term efficiency and sustainability.



