Different vegetable cultivated in India is a source of living for many people, directly or indirectly.
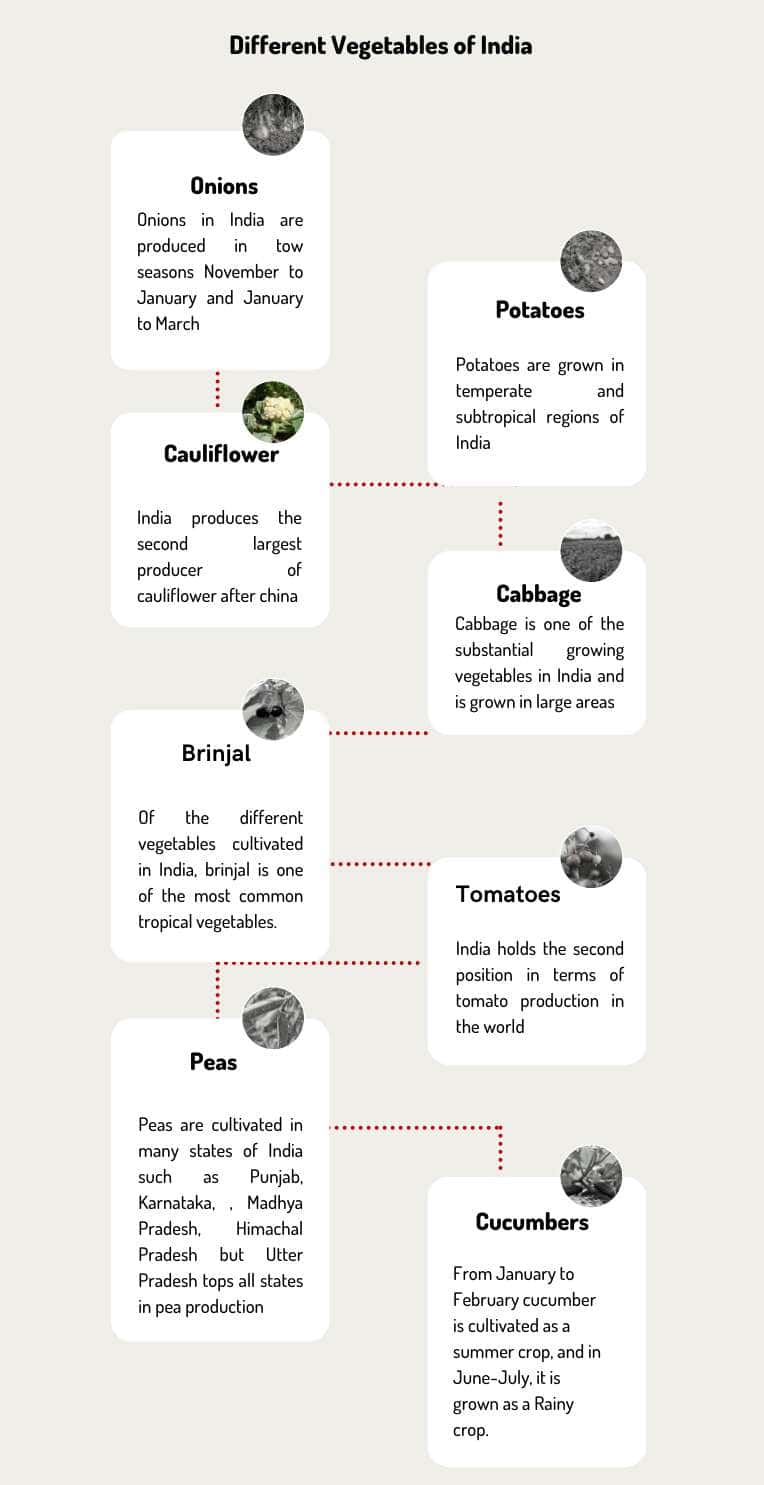
India cultivates many vegetables, such as cabbage, carrot, potato, onion, tomato, cauliflower, cabbage, beans, cucumber, peas, pumpkin, radish, mushroom, beetroot, and much more.
Regarding horticulture production, India has the second number in the world. India produces 12% of the global production of vegetables and fruits. The production of vegetables and fruits is increasing year by year.
During 2022-21 India produces 329.86 million tonnes of vegetables and fruit, the production higher than in previous years.
Vegetables have not only economic benefits but are also rich in health-benefiting nutrients. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, antioxidants, fiber, etc.
Vegetable Cultivation in India
Different vegetables cultivated in India cover about 10.86 million hectares of land. India fulfills the country’s vegetable needs and exports vegetables worth crores of rupees to foreign countries.
UAE, UK, Qatar, Oman, Nepal, Malaysia, Netherlands, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh are major countries where fresh vegetables are exported from India.
Here we look at some major cultivated and commonly used vegetables in India.
Onion Cultivation
Among the different vegetables cultivated in India are onions. Almost every household in India uses onions in their daily meals. Regarding onion production, India is the second largest producer in the world.
India produces onions in two crop cycles, November to January is the first harvesting season, and January to March is the second harvesting season.
Onion is a bulb-shaped vegetable; bulbs can be white, red, or yellow. The onion’s narrow, hollow leaves and stems enlarge and become an onion after plantation onions take 80 to 150 days to harvest.
0.39 million hectares of land are under onion cultivation in India, producing 4.30 million tonnes per year. [1]
In India, Rajasthan, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Bihar, Utter Pradesh, Gujarat, Telangana, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Odisha are central onion-producing states.
Potato Cultivation
The scientific name of the potato is Solanum tuberosum. Potatoes are grown in temperate and subtropical regions of India.
Any kitchen in India may not use potatoes; these are used in every Indian kitchen daily in one form or another. As seen in the markets, this vegetable is also used in food industries to make different chips.
India is the second largest potato producer in the world after China. Potato farming provides food for millions of people in India and a livelihood for thousands.
A considerable number of people in India are connected with potato farming. Almost every state of India grows potatoes, but the leading states are West Bangla, Utter Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Bihar, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Gujrat, Madhya Pradesh, Assam, and Punjab.
Cauliflower
Cauliflower is a cruciferous vegetable belonging to the family Brassicaceae. The edible part of this healthy vegetable is known as Curd, which consists of internodes, branches, and brackets. This vegetable is a significant crop in India.
India produces the second largest producer of cauliflower after China. The total land under different vegetables cultivated in India is 54.3 million hectares. Out of this, 4.4% is under cauliflower cultivation.
Climate, temperature, and variety of cauliflower decide its best time for sowing to form good quality curd. Cauliflower verities are grouped as early, main, and late seasons.
May to August is the sowing season for early season-harvested from September to December. September to October is the sowing season for the main season-harvested from December to January.
And October to December is the sowing season for late-season-harvested in mid-January to the end of April.
The leading cauliflower-producing states of India are West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, Gujarat, Haryana, Orissa, Chhattisgarh, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, and Assam. [2]
Also Read: Best Pest Control for Vegetable Garden
Cabbage
A significant population in India is vegetarian, and cabbage is one of the substantial growing vegetables in India and is grown in large areas. Cabbage produces a compact spherical mass made of leaves wrapped over each other.
Pride of India, Pusa Mukta Copenhagen Market, Summer Queen, Golden, Pusa Ageti, Acre, Pusa Synthetic, Quisor, Pusa Drumhead, and September Early are cabbage varieties of India.
Cabbage is commonly grown in a cool and moist climate; in plains, cabbage is produced as a winter crop. pH ranging from 5.5-6.5 is suitable for higher production.
Temperatures from 15 to 20 degrees are optimal for growing good-quality cabbage. Flowering intensity depends on plant age and period of exposure to temperatures.
0.418 million hectares of land were under cabbage cultivation in 2022, with an estimated 9.72 million metric tons of cabbage.
West Bengal, Orissa, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, and Jharkhand are the leading cabbage-producing states of India.
Brinjal
In India, brinjal has been cultivated for hundreds of years. Worldwide, brinjal is grown on 1.85 million hectares of land; in India, its cultivation occupies 0.72 million hectares.
Of the different vegetables cultivated in India, brinjal is one of the most common tropical vegetables. Brinjal can be cultivated throughout the year in plains, but its rabi crop season is the best.
Indians use brinjal as cooked vegetables in several ways. This vegetable is used as curries in Indian cousins.
It can be grown in the rainy season-June to July, winter, October to November, and summer, season-February to March.
Pusa Purple Long, Pusa Purple Cluster, Pusa Purple Round, Azad Kranti, Arka Shirish, Arka Kusumkar, Arka Nidhi, Pusa Barsati, and Pusa Uttam are the top verities of brinjal cultivated in India.
In India, brinjal is produced in many states. In Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, West Bengal, and Orissa grows brinjal on 61 % of the total land under brinjal cultivation.
Tomatoes
India holds the second position in terms of tomato production in the world. During the financial year 2022, tomato vegetable cultivation in India occupies 0.84 million hectares and produces an estimated 20 million metric tons of tomatoes.
Tomatoes are cultivated through seeds and can be cultivated on many soil types-heavy clays to sandy. Red loam, sandy soils with a pH ranging from 6.0 to 7.0, and a sound drainage system are absolute for its cultivation.
The Autumn winter crop of tomatoes is sown in June-July in November, seeds are sown for Spring Summer crops, and March-April is the sown season for hill areas.
After plantation, tomato produce is ready to harvest in 2 to 3 months. The market decides on tomato harvesting, i.e., it is carried out according to the market need.
Tomatoes are grown in several states of India. Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujrat, Odisha, West Bengal, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, and Bihar are the top-growing states of tomatoes. [3]
Peas
Peas are grown worldwide; when green, they are eaten as vegetables, and after drying, they are used as pulses.
After chickpeas and lentils, it is a popular rabi pulse of India. Pea cultivation occupies the 4th position in the area, and in production, it has the 5th position in India.
Peas are grown on many soil types-clay, sandy loan, etc. The crop’s good yield needs soil with 6 to 7.5 pH with a well-drainage system. Watery condition is not suitable for crop cultivation.
Several varieties of pea are cultivated in India, such as Prakash (IPFD 1-10), Paras, SwarnaTripti, Pant Pea-14, Pant P 13, VL-Matar-42, Pant Pea-25, Aman (IPF 5-19), Hariyal (HFP-9907 B), and Pant Pea-42.
The leading pea-producing states of India are Punjab, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra. Utter Pradesh tops all states in pea production.
Cucumbers
The cucumber is a widely grown summer vegetable among the different vegetables cultivated in India. The cucumber plant is creepy and climbs on any support it founds.
Cucumbers can be eaten raw as a salad and as cooked vegetables. Cucumbers are good for constipation.
Various soil types are used to grow cucumber ranging from sandy loam to clay, with pH from 5.5 to 6.7 and a sound drainage system suitable for good yield.
Moderate warm temperature is required to grow cucumbers. Temperatures between 25 to 35 Celsius are ideal for cucumber cultivation. Frost conditions are not suitable for this vegetable.
This vegetable is cultivated in summer and rainy crop in India. January-February cucumber is cultivated as a summer crop, and in June-July, it is grown as a Rainy crop.
Various varieties of cucumber cultivated in India are Punjab Kheera, Punjab Naveen, Pusa, and Uday, Pusa Barkha.
Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh are leading states in growing cucumbers in India.
Conclusion
Vegetables are cultivated on thousands of acres of land in India. Different vegetables cultivated in India not only provide food for thousands but also provide a livelihood. In India, thousands are connected with vegetable cultivation, selling these in the market and earning daily bread.
Different vegetable cultivation in India occupies millions of hectares of land with millions of tons of produce. India fulfills its need for vegetables and exports them to various countries worldwide.
Eating vegetables fills your stomach and provides several healthy nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, antioxidants, minerals, carbohydrates, proteins, etc.



