The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare plays a vital role in fostering agricultural development and ensuring the welfare of farmers in our country. Tasked with the formulation and execution of policies, this ministry stands as a guardian of rural livelihoods and a catalyst for sustainable farming practices.
Its role extends beyond the fields, reaching into the economic fabric of our nation, ensuring fair returns for farmers, and navigating challenges such as climate fluctuations and market dynamics.
Through a tapestry of initiatives, it strives to modernize farming, enhance food security, and create a robust support system for those who feed our nation.
In the fields and furrows, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare plants the seeds of progress, harvesting a future of prosperity for our agrarian communities
Organizational Structured of the Ministry of Agriculture
The organizational structure of the ministry of agriculture and farmers welfare consists of the following units and divisions.
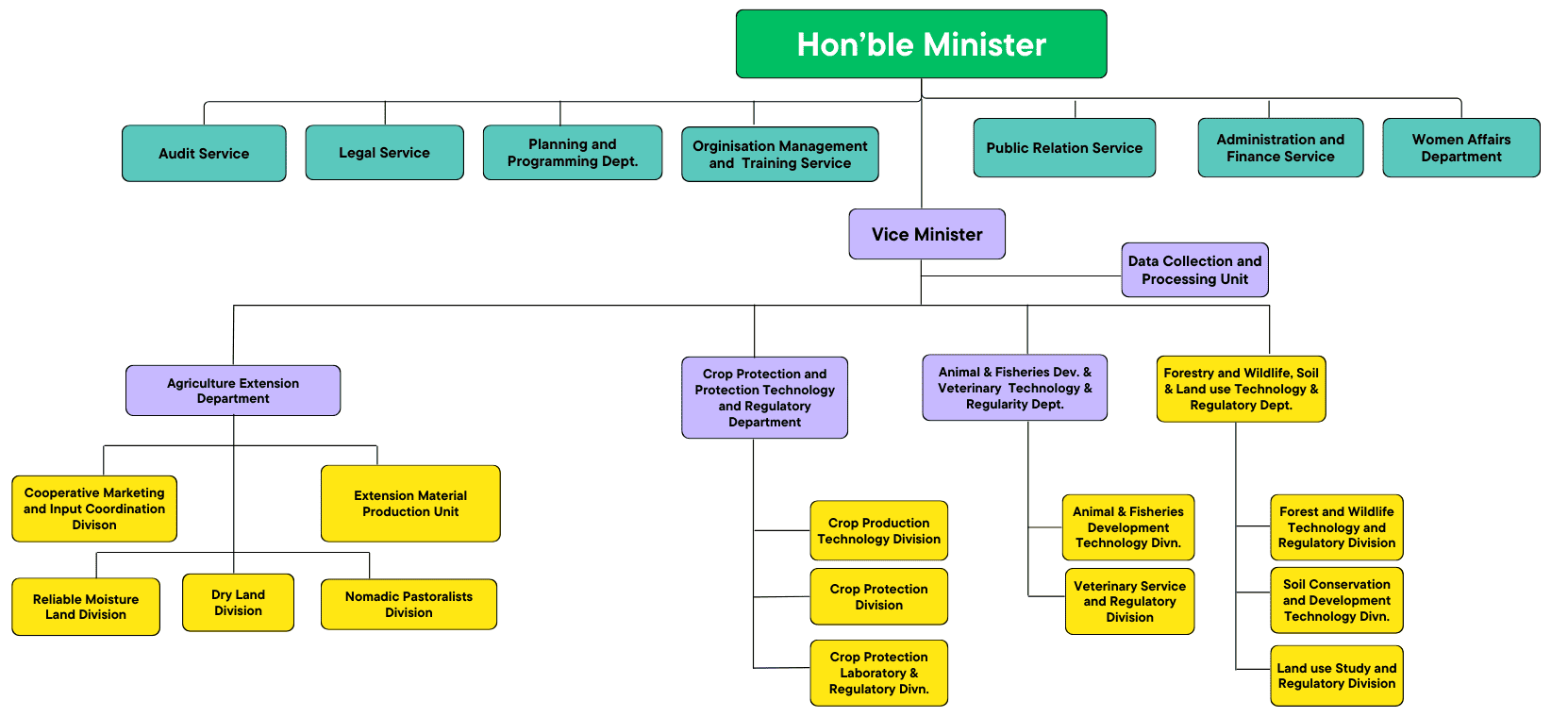 The organizational structure of our agricultural ministry is intricately designed to address the diverse needs of the agricultural sector. At the apex, the ministry is headed by the Agriculture Minister, overseeing a framework that comprises several key departments.
The organizational structure of our agricultural ministry is intricately designed to address the diverse needs of the agricultural sector. At the apex, the ministry is headed by the Agriculture Minister, overseeing a framework that comprises several key departments.
The Department of Agriculture and Cooperation focuses on policy formulation, planning, and coordination of agricultural programs. Simultaneously, the Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying, and Fisheries is dedicated to the development and regulation of livestock and fisheries.
These departments collaborate seamlessly to achieve the overarching goals of the ministry, promoting sustainable agriculture and ensuring farmer welfare. The National Institute of Agricultural Marketing operates under the ministry’s umbrella, working towards enhancing market efficiency and connecting farmers with consumers.
To achieve its goals effectively, the ministry engages in collaborative efforts with various government bodies and agencies. Close coordination with the Ministry of Finance is essential for budgetary allocations and financial support to implement agricultural schemes.
Partnership with the Ministry of Rural Development ensures synergy in rural development initiatives, creating a holistic approach. The ministry also collaborates with scientific institutions and research bodies to integrate technological advancements into agricultural practices.
Inter-ministerial committees and task forces are formed to address specific challenges, fostering a cohesive approach across government agencies. This collaborative framework underscores the ministry’s commitment to a comprehensive and integrated strategy for the holistic development of agriculture and the well-being of farmers.
Significance and Role of Agricultural Ministry
The ministry of Agricultural and farmers welfare in our country is the bedrock of rural sustenance, playing a pivotal role in both the growth of agriculture and the welfare of farmers. Its significance is deeply rooted in its multifaceted functions, aiming to address the challenges and opportunities within the agricultural landscape.
The ministry spearheads policy formulation and implementation, orchestrating initiatives to boost productivity, sustainability, and modernization of farming practices. By facilitating access to credit, insurance, and fair pricing mechanisms, it becomes the lifeline for farmers, ensuring their economic stability and safeguarding against unforeseen adversities.
In the context of agricultural development, the ministry’s role extends to promoting crop diversification, adopting advanced technologies, and fostering research and development. It serves as a catalyst for rural employment, contributing to the overall economic prosperity of the nation.
Importantly, the ministry acts as a responsive entity, tailoring its strategies to address the unique challenges faced by farmers, be it climate change, market fluctuations, or resource constraints. In essence, the Agricultural Ministry stands as the custodian of our agricultural heritage, nurturing its growth, and ensuring the well-being of the hands that till the soil.
Also Read: Different Vegetables Cultivated in India
Agricultural Ministry’s Initiatives and Programs
The ministry of agriculture has spearheaded a series of major initiatives and programs to bolster farmer support and foster agricultural development.
Among these, the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) scheme stands out, providing direct income support to small and marginal farmers. Another flagship initiative is the National Agriculture Market (eNAM), which integrates agricultural markets across states, promoting transparency and competitive pricing for farmers.
In response to challenges faced by farmers, the ministry has launched the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), an innovative crop insurance scheme.
This program mitigates the financial risks associated with crop failures due to natural calamities, ensuring farmers receive adequate compensation. Additionally, the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana promotes organic farming methods, emphasizing sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural practices.
To address water scarcity, the ministry has initiated the Per Drop More Crop scheme, encouraging efficient water management in agriculture. The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme facilitates easy access to credit for farmers, empowering them to invest in modern farming techniques and inputs.
These initiatives showcase the ministry’s commitment to tackling contemporary challenges in agriculture.
By combining financial support, technology integration, and sustainable practices, these programs aim to uplift farmers and catalyze overall agricultural development, ensuring a resilient and prosperous future for the agrarian community.
Technology and Innovation
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare has embraced technology and innovation as pivotal tools to enhance agricultural productivity and usher in a new era of efficiency in farming practices.
One notable initiative is the adoption of precision farming techniques, leveraging satellite imagery and data analytics to optimize crop management. This allows farmers to make informed decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, resulting in resource savings and improved yields.
The ministry has also championed the use of mobile applications to disseminate crucial agricultural information directly to farmers. These apps provide real-time weather updates, market prices, and expert advice, empowering farmers with knowledge to make timely and informed decisions.
Furthermore, the introduction of smart farming equipment, such as sensor-based irrigation systems and automated machinery, has streamlined cultivation processes, reducing labor intensity and increasing overall efficiency.
In the pursuit of sustainable agriculture, the ministry has encouraged the adoption of organic farming practices and agroecological approaches. These involve minimal use of synthetic inputs, promoting soil health and biodiversity.
Additionally, the ministry established several agricultural research institutes for the promotion of biotechnology in agriculture, such as genetically modified crops resistant to pests or capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions, has been explored to enhance crop resilience and productivity.
By fostering a culture of innovation and technology integration, the Ministry of Agriculture is not only modernizing farming practices but also ensuring that farmers have access to the tools and knowledge needed to thrive in an ever-evolving agricultural landscape.
Policy Framework
The Ministry of Agriculture in India has implemented a spectrum of agricultural policies aimed at fostering sustainable development, improving farmers’ livelihoods, and fortifying the overall agricultural landscape. These policies encompass a wide array of areas, ranging from crop diversification to irrigation infrastructure and market reforms.
One significant policy is the Minimum Support Price (MSP) mechanism, which guarantees farmers a minimum price for their crops, providing a safety net against market fluctuations. This policy is pivotal in ensuring economic stability for farmers and incentivizing agricultural production.
Additionally, the Crop Insurance Scheme has been introduced to mitigate the financial risks associated with crop failures due to natural calamities, offering farmers a safety net against unforeseen adversities.
The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) is another crucial policy, focusing on creating efficient water management practices through the development of irrigation infrastructure. This not only enhances agricultural productivity but also addresses water scarcity issues in various regions.
The impact of these policies on farmers is substantial. MSP ensures that farmers receive remunerative prices for their produce, providing financial security and stability.
The Crop Insurance Scheme protects farmers from income losses due to crop failure, reducing the vulnerability associated with unpredictable weather conditions. The PMKSY, by enhancing irrigation facilities, contributes to increased crop yields and overall agricultural productivity.
Collectively, these policies reflect the ministry’s commitment to creating an enabling environment for farmers, ensuring sustainable agricultural practices, and fortifying the resilience of the agricultural sector in the face of challenges.
Financial Support and Subsidies
The agricultural ministry for farmers has instituted robust financial support mechanisms and subsidies to fortify the economic foundations of farmers.
One key initiative is the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system, which ensures targeted and timely financial assistance directly to the bank accounts of eligible farmers. This streamlines the distribution of subsidies, reducing inefficiencies and leakages in the system.
Various subsidies are extended to farmers, covering aspects such as fertilizers, seeds, irrigation, and machinery. The eligibility criteria for availing these benefits often include landholding size, type of crops cultivated, and adherence to sustainable agricultural practices.
Typically, small and marginal farmers are prioritized to ensure inclusivity and equitable distribution of resources.
The process of availing these benefits involves farmers registering with local agricultural offices and providing requisite documentation, including land records and proof of cultivation. Once verified, subsidies are disbursed directly to the farmers’ bank accounts.
The introduction of digital platforms and online application processes has further simplified and expedited the disbursement process, ensuring that farmers can access financial support efficiently.
These financial support mechanisms play an important role in enhancing the economic well-being of farmers, enabling them to invest in modern farming practices, purchase quality inputs, and navigate the challenges of agricultural production.
By promoting transparency and inclusivity, the ministry’s subsidy programs contribute to the overall development and sustainability of the agricultural sector.
Challenges Faced by Farmers
Farmers in our region encounter a myriad of challenges, and the Ministry of Agriculture has undertaken strategic measures to alleviate these hardships.
Climate change poses a significant threat, leading to erratic weather patterns, unpredictable rainfall, and extreme temperatures. In response, the ministry has initiated programs to promote climate-resilient agricultural practices, including the adoption of drought-resistant crops and water-efficient irrigation systems.
Additionally, the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture focuses on enhancing soil health and promoting agroforestry, mitigating the impact of climate change on crop yields.
Market fluctuations represent another obstacle for farmers, impacting income stability. The ministry has implemented the eNAM (Electronic National Agriculture Market) platform, fostering a unified market space and reducing the influence of intermediaries. This ensures fair prices for farmers and facilitates better market access.
Pest outbreaks are a perennial concern affecting crop yields. The ministry has instituted integrated pest management strategies, advocating for the judicious use of pesticides, promoting natural predators, and encouraging crop diversification to minimize the risk of widespread pest infestations.
Through these targeted initiatives, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare strives to fortify the resilience of farmers in our region.
By addressing climate-related uncertainties, market challenges, and pest threats, the ministry aims to create a sustainable and supportive environment for farmers, safeguarding their livelihoods and bolstering the overall stability of the agricultural sector.
Future Plans and Vision
The agriculture ministry in India envisions a dynamic future for agricultural development and farmer welfare, with an array of upcoming policies and projects poised to shape the trajectory of the sector.
A cornerstone of their future plans is the continued emphasis on sustainable farming practices and environmental stewardship. This includes the promotion of organic farming, agroecological approaches, and the integration of eco-friendly technologies to enhance productivity without compromising long-term soil health.
In line with the government’s commitment to doubling farmers’ income, the ministry is set to roll out targeted financial support schemes and credit facilities. These initiatives aim to empower farmers economically, providing them with the necessary resources to invest in modern agricultural techniques and diversify their income streams.
Furthermore, the ministry is actively exploring partnerships with research institutions and private entities to foster innovation in agriculture. Collaborative projects focusing on precision farming, smart agriculture, and the development of climate-resilient crop varieties are in the pipeline, promising to revolutionize farming practices and enhance overall productivity.
As part of their vision for farmer welfare, the ministry is working on strengthening social security nets. This includes comprehensive insurance coverage and pension schemes tailored to the needs of the farming community, ensuring that farmers have a safety net to fall back on during challenging times.
In essence, the future plans of the ministry of agriculture encapsulate a holistic approach, balancing economic prosperity for farmers, sustainable agricultural practices, and technological innovation to build a resilient and thriving agrarian landscape.
Success Stories
Across the landscape of our agricultural communities, success stories and case studies illuminate the tangible impact of the ministry of agriculture’s initiatives and policies.
Take, for instance, the story of a smallholder farmer who, through the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana, received timely compensation for crop damage caused by unseasonal rains. This financial support not only alleviated the immediate economic burden but also enabled the farmer to reinvest in the next agricultural season, fostering sustainability.
In another instance, a farmer participating in the eNAM platform experienced a transformative shift in income dynamics. By directly connecting with buyers, the farmer secured better prices for produce, reducing dependency on middlemen and enhancing overall profitability.
This not only bolstered individual economic well-being but also contributed to the prosperity of the entire village.
Moreover, success stories abound in the realm of technology adoption. Farmers embracing precision farming techniques witnessed significant improvements in crop yields and resource efficiency. Through the dissemination of knowledge via mobile applications, farmers are now better equipped to make informed decisions, leading to increased productivity and income.
These success stories underscore the tangible positive outcomes of the ministry’s initiatives, creating a ripple effect that transcends individual farmers to uplift entire rural communities. The interventions are not just about cultivation; they are about cultivating sustainable livelihoods, resilience, and prosperity in the agrarian heartland.
Conclusion
The ministry of agriculture and farmers welfare plays a vital role in supporting and uplifting the farming community.
By implementing various schemes and initiatives, the ministry aims to improve agricultural practices, enhance farmer welfare, and contribute to the overall growth of the agricultural sector. The focus on sustainable and inclusive development is evident in the efforts to provide financial assistance, modernize farming techniques, and ensure the availability of essential resources.
The ministry’s commitment to addressing the diverse needs of farmers reflects a genuine effort to boost rural economies and strengthen the backbone of our nation.
As we acknowledge the significance of agriculture in our daily lives, the agricultural ministry stands as a crucial entity dedicated to fostering a thriving agricultural landscape for the benefit of our farmers and the nation as a whole.



