Organic farming (जैविक खेती) is transforming modern agriculture by focusing on sustainability, soil health, and eco-friendly practices. The components of organic farming ensure that crops grow naturally without harming the environment.
Unlike conventional methods that rely on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, it nurtures the land using natural compost, crop rotation, and biological pest control.
Organic farming approach goes beyond just growing crops. It restores soil fertility, conserves water, and reduces pollution. Many farmers are now shifting to organic methods to combat climate change and preserve biodiversity. However, maintaining a balanced organic system requires several essential elements.
Understanding the vital components of organic farming is crucial for sustaining long-term agricultural productivity. From soil enrichment to pest management, each component plays a key role in ensuring healthier food and a greener planet.
Understanding Organic Farming
Organic farming (जैविक खेती) is a natural and sustainable approach to agriculture that avoids synthetic chemicals, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and artificial fertilizers.
Instead, it relies on ecological processes, biodiversity, and cycles adapted to local conditions. The primary goal is to maintain soil fertility, conserve water, and promote a balanced ecosystem.
Unlike conventional farming, which often depletes soil nutrients and relies heavily on chemical inputs, organic farming fosters long-term sustainability. It enhances soil health through composting, crop rotation, and biological pest control.
The components of organic farming work together to create a self-sustaining system that reduces environmental harm while producing high-quality food. By focusing on natural growth methods, organic farming ensures a safer and healthier food supply for future generations.
Organic Farming: A Return to Nature
Modern agriculture has long depended on synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically engineered crops. While these methods increase yields, they also disrupt natural ecosystems, harm biodiversity, and degrade soil health.
Organic farming takes a different approach, working in harmony with nature rather than against it. By using natural fertilizers, crop diversity, and biological pest control, it maintains soil fertility and ecosystem stability.
One of the vital components of organic farming is soil enrichment. Organic farmers use compost, manure, and cover crops to replenish nutrients naturally. This enhances soil structure, prevents erosion, and increases water retention.
Another key aspect is biodiversity. Instead of monoculture farming, organic practices encourage crop diversity, which reduces the risk of pests and diseases.
Moreover, organic farming supports pollinators like bees and butterflies, which are crucial for food production. By avoiding harmful pesticides, it preserves insect populations essential for pollination.
Sustainable water management, such as rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation, further strengthens organic farming’s commitment to nature. This holistic approach not only produces healthier crops but also safeguards the environment for future generations.
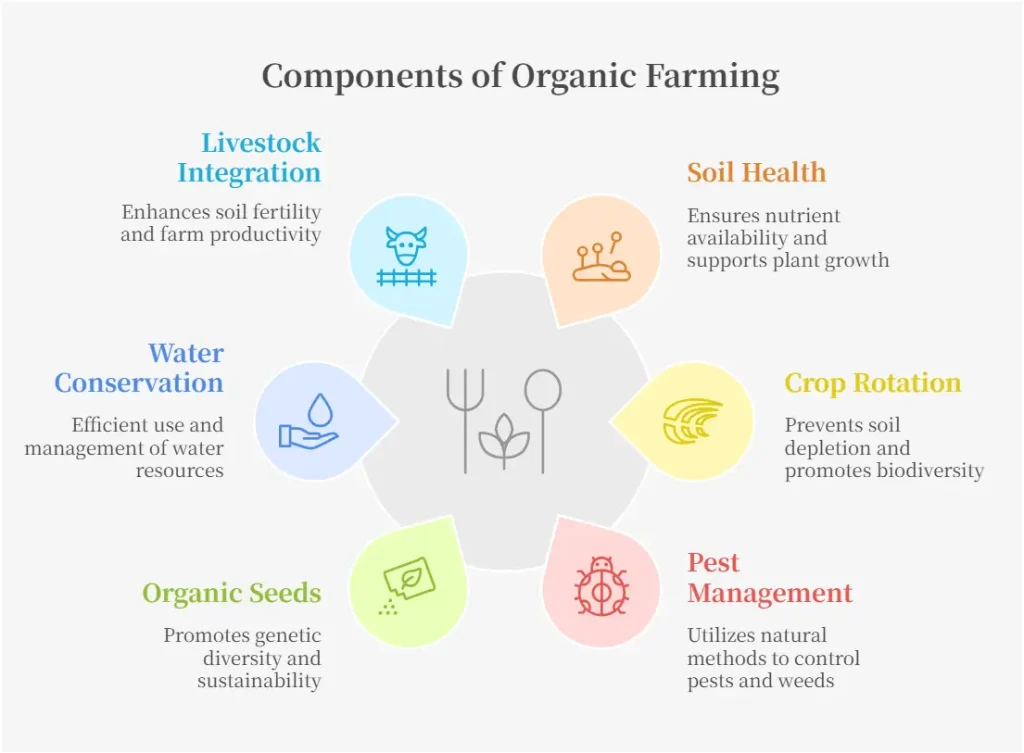
Essential Components of Organic Farming
Organic farming depends on several key components that ensure long-term sustainability and productivity. These vital components of organic farming create a balanced agricultural system that protects the environment while producing nutritious food.
Soil Health and Organic Matter
Healthy soil is the foundation of organic farming. It supports plant growth, retains moisture, and enhances nutrient availability. Farmers use compost, manure, and green cover crops to maintain soil fertility naturally.
Organic matter improves soil structure, reduces erosion, and promotes beneficial microbial activity, ensuring crops thrive without synthetic fertilizers.
Crop Rotation and Diversity
Rotating crops prevents soil depletion and disrupts pest life cycles. Different crops have unique nutrient needs, so alternating them helps maintain soil balance. Diversity also reduces the spread of diseases and weeds.
By growing multiple plant species, farmers create resilient ecosystems that improve productivity and sustainability.
Natural Pest and Weed Management
Instead of chemical pesticides, organic farming relies on biological controls like beneficial insects, companion planting, and mulching. For instance, ladybugs and praying mantises help control aphid populations, while mulch suppresses weed growth.
Intercropping—growing different plants together—also prevents pest infestations and enhances biodiversity.
Organic Seeds and Planting Materials
Using non-GMO, chemical-free seeds is essential in organic farming. Traditional and heirloom seed varieties often show greater resilience to local conditions. These seeds adapt to climate changes and pests, making farming more sustainable.
Additionally, organic certification ensures that seeds remain free from synthetic treatments, preserving natural genetic diversity.
Also Read: Organic Agriculture for Sustainable Food Production
Water Conservation and Management
Efficient water use is crucial in organic farming. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, reducing waste and evaporation. Rainwater harvesting captures and stores water for dry periods.
By preventing water pollution from agricultural runoff, organic farming helps protect rivers, lakes, and groundwater sources.
Livestock Integration in Organic Farming
Ethical livestock management plays a significant role in organic agriculture. Animals raised in organic systems graze on natural pastures, receive organic feed, and are treated humanely.
Their manure is used as an organic fertilizer, enriching the soil with essential nutrients. This integration creates a closed-loop system, reducing waste and improving overall farm efficiency.
By incorporating these fundamental practices, organic farming remains a sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to food production.
The combined effect of soil health, biodiversity, pest control, water management, and ethical livestock practices ensures that agriculture continues to thrive in balance with nature.
Challenges in Organic Farming
Organic farming offers many benefits, but it also comes with challenges. One major issue is the high initial cost. Organic farmers invest in natural fertilizers, biological pest control, and organic certification, which can be expensive.
Additionally, the market for organic produce is still growing, and farmers may struggle to find buyers willing to pay a premium.
In the early transition period, lower yields are common. Since organic farming avoids synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, crops may take time to adjust to natural inputs.
Weeds and pests can also be harder to control without chemical solutions. Farmers must rely on crop rotation, mulching, and natural predators, which require patience and effort.
Another challenge is the limited availability of organic seeds and inputs. Many traditional markets mainly supply chemically treated seeds, forcing organic farmers to search for certified alternatives.
Despite these obstacles, the components of organic farming like soil health, biodiversity, and eco-friendly techniques make it a long-term solution. By improving practices and increasing awareness, farmers can overcome these hurdles and make organic farming more sustainable.
Conservation and Sustainability in Organic Farming
Organic farming plays a crucial role in environmental conservation. Unlike conventional farming, which relies on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, organic methods work with nature. This helps reduce soil erosion, maintain biodiversity, and protect water quality.
By using compost, cover crops, and crop rotation, farmers enhance soil fertility without harming the ecosystem.
One of the vital components of organic farming is its ability to mitigate climate change. Organic farming reduces greenhouse gas emissions by avoiding synthetic fertilizers, which release nitrous oxide—a potent greenhouse gas.
Additionally, practices like agroforestry and carbon sequestration help absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere.
Organic farming also follows strict certifications and standards. Organizations like USDA Organic, EU Organic, and India’s NPOP ensure that farmers meet sustainability guidelines. These certifications help consumers trust organic products and support eco-friendly agriculture.
With continued efforts, organic farming can lead the way in building a more sustainable food system.
Global Perspectives: Organic Farming Across the World
Organic farming is growing worldwide as more people choose healthier and eco-friendly food options. In India, organic farming is expanding due to government incentives and a growing market for organic products. Many farmers use traditional methods, making the transition easier.
In the European Union (EU), organic farming is widely supported. Strict regulations ensure that organic products meet high-quality standards. Countries like Germany and France have large organic food markets, with consumers willing to pay more for sustainable produce.
The United States has one of the largest organic markets. Many farmers switch to organic due to high demand and better prices. Government programs also offer support for transitioning farmers.
As global awareness grows, more countries are investing in organic farming to ensure food security and environmental sustainability.
Organic vs. Conventional Farming: Why the Shift Matters
| Features | Organic Farming | Conventional Farming |
| Use of Chemicals | Avoids synthetic fertilizers and pesticides | Relies on chemical inputs |
| Soil Health | Uses compost and crop rotation to improve soil fertility | Often depletes soil nutrients |
| Pest Control | Relies on natural predators, mulching, and companion planting | Uses chemical pesticides |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces pollution and promotes biodiversity | Can lead to soil degradation and water pollution |
| Health Benefits | Produces chemical-free, nutrient-rich food | May contain pesticide residues |
| Long-Term Sustainability | Focuses on ecological balance and self-sustaining methods | Often prioritizes short-term productivity |
Success Stories: How Farmers Are Thriving with Organic Practices
Many farmers worldwide have successfully transitioned to organic farming and are seeing great results. In Sikkim, India, the government made the entire state 100% organic, boosting farmers’ incomes and improving soil health. Today, Sikkim is a global example of sustainable agriculture.
In California, USA, many vineyards have switched to organic farming, reducing chemical use while maintaining high-quality grape production. Similarly, small-scale farmers in Kenya use organic methods to grow coffee and vegetables, leading to higher profits and healthier communities.
These success stories show that organic farming is not just a trend but also a viable solution for long-term sustainability. By adopting components of organic farming, farmers can increase productivity while protecting the environment.
Conclusion
Organic farming is more than just an agricultural method—it is a movement towards a healthier and more sustainable future. By focusing vital on components of organic farming , such as soil health, biodiversity, and ethical practices, farmers can create a system that benefits both people and the planet.
Though challenges exist, the long-term advantages outweigh the difficulties. Consumers can also support organic farming by choosing organic products and spreading awareness.
Together, we can build a future where agriculture works in harmony with nature, ensuring a safer and healthier food system for generations to come.












