Sustainable organic agriculture is shaping the future of food production. It relies on natural farming methods that protect soil, water, and biodiversity. By avoiding synthetic chemicals, it ensures healthier food while reducing environmental damage.
Unlike conventional farming, which depletes resources, organic agriculture supports long-term sustainability.
Farming without harmful pesticides and artificial fertilizers helps maintain soil fertility and water purity. Sustainable organic agriculture also promotes biodiversity, allowing beneficial insects and microorganisms to thrive. This balance strengthens ecosystems and improves crop resilience.
With rising concerns about food safety and climate change, many people are turning to organic farming. It offers a reliable way to produce nutritious food while safeguarding the planet. This article explores its meaning, benefits, challenges, and global impact, highlighting why it is essential for a sustainable future.
What is Organic Agriculture?
Organic agriculture is a farming system that focuses on natural processes to grow crops and raise livestock. It avoids synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Instead, farmers use compost, crop rotation, and biological pest control to maintain soil health and biodiversity.
Unlike conventional farming, which relies on chemical inputs for higher yields, organic agriculture nurtures the land. It improves soil fertility by using natural amendments like manure and cover crops.
Sustainable organic agriculture also encourages beneficial insects and microorganisms, reducing the need for harmful pesticides.
One of its key goals is to create a balanced ecosystem. Healthy soils lead to stronger plants, which require fewer external inputs. This approach reduces chemical pollution and improves food quality. By limiting artificial substances, organic farming ensures that fruits, vegetables, and grains retain their natural nutrients.
In addition to environmental benefits, organic agriculture promotes long-term food security. Healthier soils produce crops year after year without degrading the land. As global demand for safe and nutritious food grows, sustainable organic agriculture offers a reliable way to feed the population while protecting the environment.
Organic Agriculture: A Sustainable Food Path
Modern farming often prioritizes high yields over environmental health. Conventional agriculture uses synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which harm the soil and water.
These chemicals disrupt ecosystems, kill beneficial organisms, and contribute to climate change. Intensive farming also depletes nutrients from the soil, making land less productive over time.
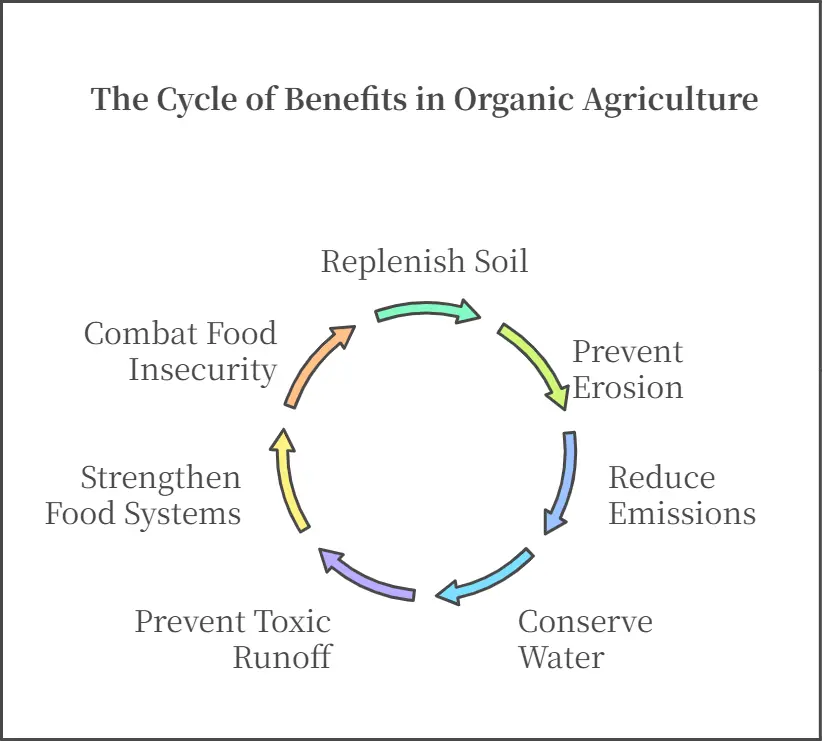
Sustainable organic agriculture offers a solution to these problems. By using natural fertilizers like compost and manure, it replenishes the soil. Crop rotation and cover crops prevent erosion and maintain soil fertility.
This method also reduces greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing the use of synthetic chemicals and fossil fuel-based inputs.
Water conservation is another major advantage. Organic farming practices, such as mulching and intercropping, help retain moisture in the soil. This reduces the need for excessive irrigation, which is crucial in water-scarce regions. Additionally, organic methods prevent toxic runoff, keeping rivers and lakes clean.
Organic agriculture strengthens food systems by creating resilient crops. Plants grown in healthy, chemical-free soil develop better resistance to pests and diseases. This reduces reliance on pesticides while ensuring stable food production.
A shift toward sustainable organic agriculture can help combat food insecurity while preserving the planet for future generations.
Benefits of Organic Agriculture
Organic agriculture offers numerous advantages for the environment, economy, and human health.
Environmental Benefits:
Preserves Soil Fertility– Organic farming builds healthy soils through composting, crop rotation, and green manure. This prevents soil degradation and maintains productivity.
Enhances Biodiversity– By avoiding harmful chemicals, organic farms create a habitat for beneficial insects, birds, and soil organisms. Pollinators like bees thrive in organic fields.
Reduces Water Pollution– Without synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, organic farming prevents toxic runoff into rivers and lakes. This protects freshwater sources and aquatic life.
Also Read: Why Organic Farming is Essential Today?
Economic and Social Benefits:
Empowers Farmers– Organic farming reduces reliance on expensive chemical inputs, making agriculture more cost-effective and sustainable.
Boosts Rural Economies– The demand for organic products creates new market opportunities, supporting small farmers and local businesses.
Provides Safer Food– Consumers benefit from pesticide-free produce rich in essential nutrients, supporting overall well-being.
Human Health Benefits:
Reduces Chemical Exposure– Organic food is free from synthetic pesticides and artificial preservatives, lowering health risks.
Higher Nutritional Value– Studies show that organic produce contains more antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals compared to conventionally grown food.
By embracing organic agriculture, societies can improve food security, protect ecosystems, and promote healthier lifestyles. Sustainable organic agriculture is a step toward a cleaner, safer, and more resilient food system.
Challenges in Sustainable Organic Agriculture
Sustainable organic agriculture offers many benefits, but it also comes with challenges. One major issue is the higher initial cost. Organic farming requires natural compost, organic seeds, and eco-friendly pest control, which can be expensive.
Additionally, farmers often face lower short-term yields since organic methods take time to improve soil health.
Another challenge is the risk of pests and diseases. Without synthetic pesticides, organic farmers rely on crop rotation, companion planting, and biological pest control.
However, these methods may not always prevent infestations, leading to potential crop losses. Weather conditions, such as heavy rains or droughts, can also increase pest outbreaks.
Limited government support and market accessibility further complicate organic agriculture. Many policies favor large-scale conventional farms, making it difficult for organic farmers to compete.
In some regions, certification costs are high, discouraging small-scale producers. Expanding access to organic markets and improving policies can help organic farmers thrive.
Examples of Organic Agriculture
Organic agriculture uses various methods to maintain soil health and protect ecosystems. Here are some key examples:
Agroforestry
Agroforestry combines trees and crops on the same land. Trees provide shade, prevent soil erosion, and enrich the soil with organic matter. This method also supports biodiversity by creating habitats for birds and beneficial insects.
Crop Rotation & Cover Cropping
Crop rotation improves soil fertility and reduces pests. Farmers plant different crops in the same field each season to balance nutrients and prevent soil depletion. Cover crops, such as legumes and clover, protect the soil from erosion and naturally add nitrogen.
Organic Livestock Farming
Sustainable organic agriculture also includes ethical livestock practices. Organic farmers raise animals on natural diets without synthetic hormones or antibiotics. They provide free-range environments that improve animal welfare and reduce stress-related diseases.
No-Till Farming
No-till farming helps preserve soil structure and increase carbon storage. Instead of plowing, farmers leave crop residues on the field, which enhances moisture retention and prevents erosion. This method supports long-term soil health while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
By using these techniques, organic agriculture promotes sustainability, biodiversity, and healthier food production.
Conservation Efforts in Organic Agriculture
Sustainable organic agriculture aligns with conservation efforts by reducing environmental impact and promoting long-term ecosystem health. By avoiding synthetic chemicals, organic farming prevents soil degradation and water pollution.
It also enhances biodiversity by creating habitats for beneficial insects, birds, and soil organisms.
Several global initiatives support organic conservation. Organic certifications, such as USDA Organic and EU Organic, ensure farms meet sustainability standards. Eco-labeling helps consumers identify organic products, encouraging demand for sustainable farming.
Additionally, policies like sustainable land management and regenerative farming programs promote responsible agricultural practices.
Organic agriculture also plays a role in climate change mitigation. No-till farming and cover cropping improve soil’s ability to store carbon, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable organic agriculture provides a nature-based solution to food production while preserving the environment for future generations.
Global Perspectives on Organic Agriculture
Organic agriculture is expanding worldwide as more countries recognize its benefits. In Europe, nations like Germany and France have strong organic farming policies, offering subsidies to encourage sustainable practices. Organic food demand in North America continues to grow, with the U.S. leading in organic farmland expansion.
In Asia, countries like India and China are investing in organic agriculture. India promotes natural farming through government initiatives, while China is increasing organic certification programs. These efforts support sustainable organic farming while reducing reliance on chemical-intensive farming.
International organizations, such as the FAO and IFOAM, advocate for organic policies. Sustainable organic agriculture is now included in global discussions on food security and climate action. As demand for healthier and eco-friendly food rises, organic agriculture is shaping the future of sustainable farming.
Future of Sustainable Organic Agriculture
Innovations Shaping Organic Farming:
AI and Technology in Organic Pest Control and Soil Monitoring: Sustainable organic agriculture is evolving with the help of technology. AI-powered systems can identify pests early, reducing crop loss without chemicals. Smart soil sensors also help farmers track moisture and nutrient levels, improving plant health naturally.
Vertical Farming and Urban Organic Gardens: With limited farmland, vertical farming is a game-changer. It allows crops to grow in stacked layers, using less space and water. Urban organic gardens also bring fresh, chemical-free food closer to people, making organic agriculture more accessible.
Role of Consumers in Supporting Organic Agriculture:
Choosing Certified Organic Products: Consumers play a vital role in promoting organic farming. By buying certified organic products, they support farmers who use eco-friendly methods. This demand encourages more farms to adopt sustainable practices.
Encouraging Farm-to-Table Movements: The farm-to-table movement strengthens local organic agriculture. When people buy directly from farmers’ markets, they reduce food miles and support small organic farms. This shift leads to fresher, healthier food while benefiting the environment.
Conclusion
Organic agriculture is key to building a sustainable food system. It preserves soil health, protects water sources, and promotes biodiversity. Unlike conventional farming, it avoids harmful chemicals, ensuring safer food and a healthier planet.
Organic agriculture also supports economic growth. It creates jobs in organic farming, processing, and distribution. Additionally, it enhances food security by encouraging local food production and reducing reliance on synthetic inputs.
As more people recognize the benefits, the future of organic farming looks promising. Governments, businesses, and consumers must work together to expand sustainable organic agriculture worldwide. With innovation and awareness, organic farming can help create a greener, healthier future for all.












